How Clogged Pores Contribute to Acne Formation
Clogged pores play a significant role in the development of acne, a common skin condition. Let’s explore the correlation between clogged pores and acne formation.
1. Role of Clogged Pores in Acne
Clogged pores, caused by dead skin cells, excess oil, or debris, form the initial stage of acne development by obstructing hair follicles. This blockage creates an ideal environment for acne formation.
2. Formation of Blackheads and Whiteheads
When pores are partially blocked, they result in blackheads (open comedones), whereas complete blockage leads to whiteheads (closed comedones), both being common acne types originating from clogged pores.
3. Bacterial Involvement and Inflammation
Clogged pores create a breeding ground for Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), a bacteria found on the skin. When trapped within blocked pores, this bacterium multiplies, triggering inflammation and contributing to acne formation.
4. Transition to Inflammatory Acne
If the clogged pore becomes inflamed due to bacterial activity or other factors, it can progress into inflammatory acne, including papules, pustules, nodules, or cysts.
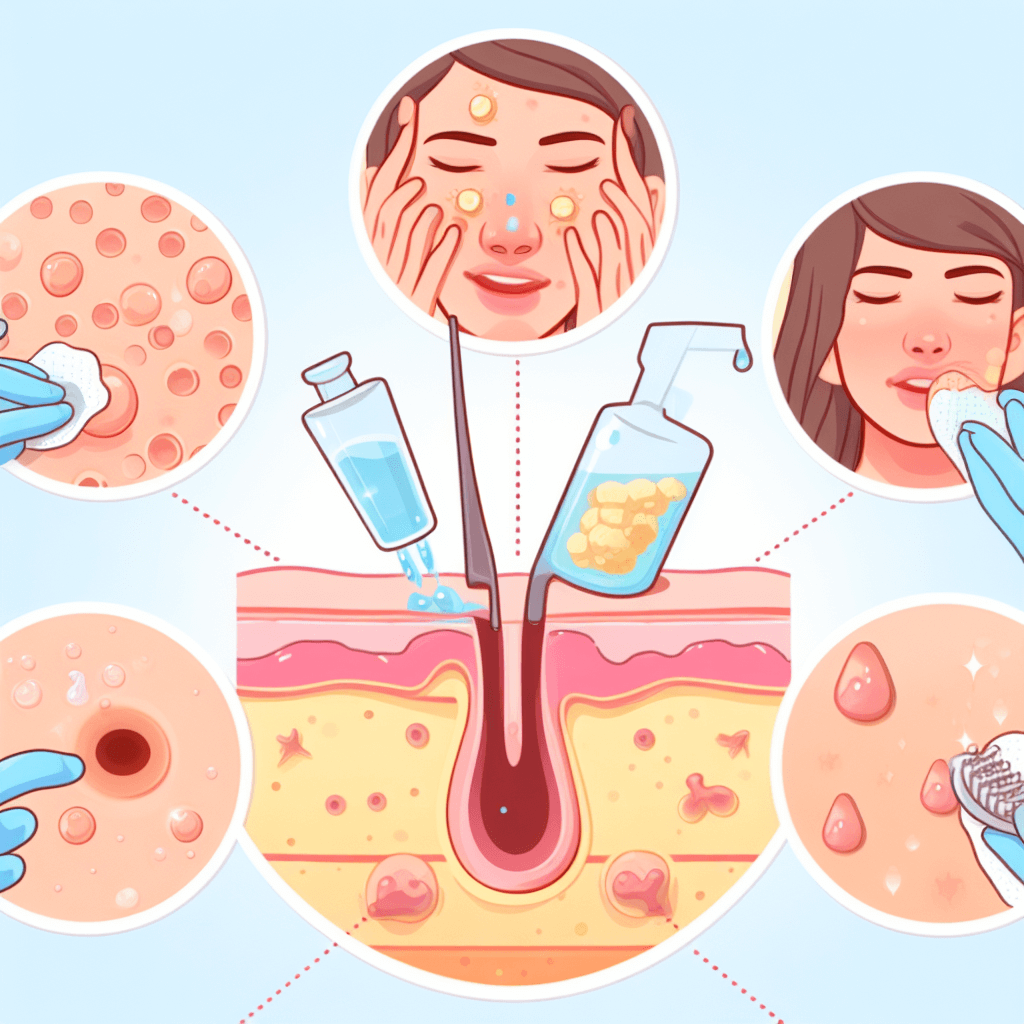
5. Preventive Measures and Management
A consistent skincare routine involving gentle cleansing, exfoliation, and the use of non-comedogenic products helps prevent and manage clogged pores, thereby reducing the risk of acne formation. Seeking professional guidance and checking pore clogging ingredients for persistent acne concerns is advisable.
Final Overview
Clogged pores serve as the primary trigger for acne formation. Understanding their role in acne development underscores the importance of effective skincare practices in preventing and managing acne.